pipeline
{
agent { label 'master'}
stages{
stage('t1'){
steps {
timeout(time: 10, unit: 'SECONDS') {
sh 'sleep 5'
sh 'echo t1'
}
}
}
stage('t2'){
steps {
sh 'echo t2'
}
}
}
}Author: Alok
nohup alternative for windows in Jenkins
1.Run windows batch command in background using start
pipeline
{
agent {
label 'master'
}
stages{
stage ('windows-nohup')
{
steps
{
bat """set JENKINS_NODE_COOKIE=dontKillMe && start /min COMMAND_TO_RUN """
}
}
}
}2.Run windows batch command in background with logs in jenkins workspace with batch and powershell
pipeline
{
agent {
label 'master'
}
stages{
stage ('windows-nohup')
{
steps
{
//copy the command to test.bat file
bat """echo COMMAND_TO_RUN REPLACE COMMAND.log > test.bat"""
//replace the REPLACE with append symbol(>)
powershell 'Get-Content test.bat | ForEach-Object { $_ -replace "REPLACE", " > " } | Set-Content test2.bat'
//run the test2.bat in background
bat 'set JENKINS_NODE_COOKIE=dontKillMe && start /min test2.bat ^& exit'
//logs will be available at workspace COMMAND.log
//Example
/*
bat """echo C:\\java8\\bin\\java -jar core.jar --config=test.json REPLACE java.log > test.bat"""
powershell 'Get-Content test.bat | ForEach-Object { $_ -replace "REPLACE", " > " } | Set-Content test2.bat'
bat 'more test2.bat'
bat 'set JENKINS_NODE_COOKIE=dontKillMe && start /min test2.bat ^& exit'
*/
}
}
}
}Github webhook integration with Jenkins
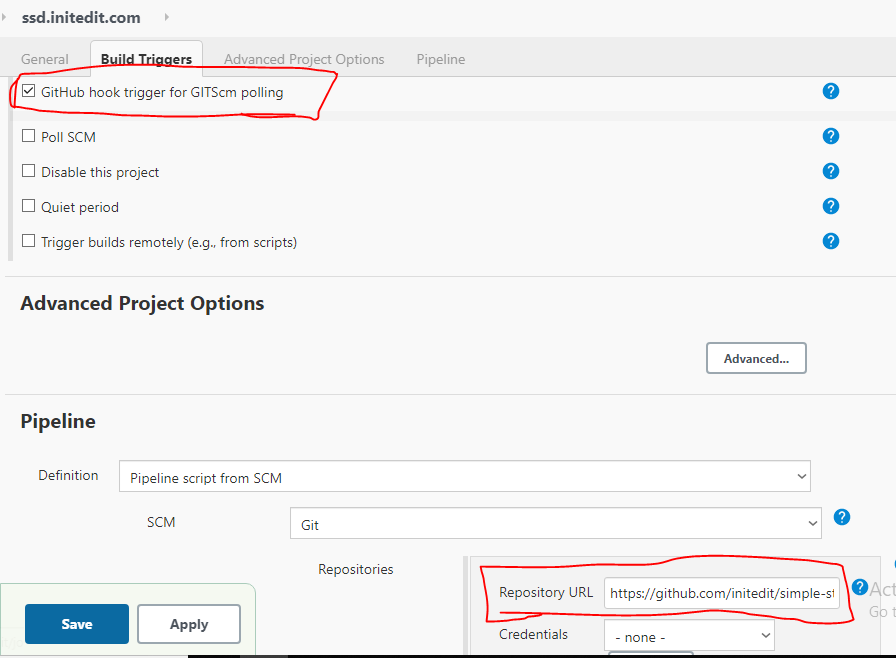
1.Project > Configure > check github hook trigger and add repository URL
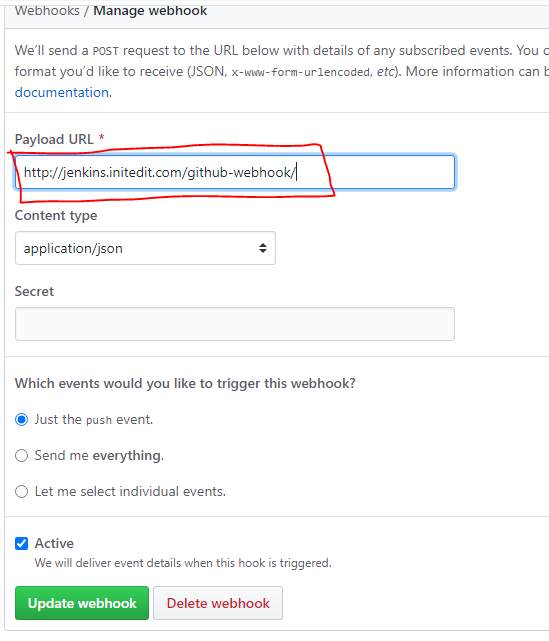
2.On Github Project > settings > Webhooks > Add webhook
Openfaas – serverless deployment with k8
1.Create serverless python3 deployment
faas-cli new --lang python3 python-fn --gateway http://192.168.0.183:31112 --prefix=192.168.0.183:30500/python-fn–prefix = Docker private repository
–gateway = Openfass gateway server
2.It will create the python-fn directory and python-fn.yml file
3.Write your python code inside python-fn/handler.py
def handle(req):
"""handle a request to the function
Args:
req (str): request body
"""
print("hola-openfaas")
return req
4.Build / Push / Deploy
faas-cli build -f python-fn.ymlfaas-cli push -f python-fn.ymlexport OPENFAAS_URL=http://192.168.0.183:31112
faas-cli login --password "YOUR_Openfaas_PASSWORD"faas-cli deploy -f python-fn.yml5. Remove
faas-cli remove -f python-fn.yml
rm -rf python-fn*Openfaas installation in k8
curl -sL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh
git clone https://github.com/openfaas/faas-netes
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openfaas/faas-netes/master/namespaces.yml
PASSWORD=$(head -c 12 /dev/urandom | shasum| cut -d' ' -f1)
kubectl -n openfaas create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=basic-auth-user=admin \
--from-literal=basic-auth-password="$PASSWORD"
cd faas-netes
kubectl apply -f ./yaml
nohup kubectl port-forward svc/gateway -n openfaas 31112:8080 &
export OPENFAAS_URL=http://192.168.0.183:31112
echo -n "$PASSWORD" | faas-cli login --password-stdin
echo "$PASSWORD"kubernetes Highly Available clusters Using 3 Master node
1. Setup TCP load balancer using nginx (192.168.0.50)
load_module /usr/lib64/nginx/modules/ngx_stream_module.so;
events { }
stream {
upstream kapi {
server 192.168.0.51:6443;
server 192.168.0.52:6443;
server 192.168.0.53:6443;
}
server {
listen 8888;
proxy_pass kapi;
}
}2. Run below command on all master node
yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl docker
systemctl enable kubelet
systemctl start kubelet
systemctl enable docker
systemctl start docker3. Run below command on 192.168.0.51
kubeadm init --control-plane-endpoint "192.168.0.50:8888" --upload-certsIt will generate command to add other master node and worker node
4.Join other 2 master (192.168.0.51, 192.168.0.52)
kubeadm join 192.168.0.50:8888 --token hvlnv8.6r90i8d04cs23sii \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:bc6fe39f98c7ae6cd8434bd8ade4eb3b15b45e151af37595e4be0a9fdfcfdcc4 \
--control-plane --certificate-key 3659353b0a256650fb0c1a0357cb608d07e3bdc8ce8b64fa995bcb814c131fa6Note : Token will be differ
5.Get the info of cluster
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodeSkip stages in Jenkins
stages {
def skip_stage = 'skip'
pipeline
{
agent {
label 'master'
}
parameters {
string(name: 'skip_stage', description: 'skip stage', defaultValue: 'skip')
}
stages
{
stage("test") {
when {
expression { skip_stage != "skip" }
}
steps {
echo 'This will never run'
}
}
}
}More when condition : https://gist.github.com/merikan/228cdb1893fca91f0663bab7b095757c
Prometheus and Grafana on Kubernetes with nfs persistent volume
Prometheus-k8.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: prometheus-deployment
labels:
app: prometheus
env: prod
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus
env: prod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
env: prod
spec:
containers:
- name: prometheus-container
image: prom/prometheus
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
subPath: prometheus.yml
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
mountPath: /prometheus
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: prometheus-conf
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
nfs:
server: 192.168.0.184
path: "/opt/nfs1/prometheus"
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: prometheus-service
labels:
app: prometheus
env: prod
spec:
selector:
app: prometheus
env: prod
ports:
- name: promui
protocol: TCP
port: 9090
targetPort: 9090
nodePort: 30090
type: NodePortCreate prometheus.yml config-map file
kubectl create configmap game-config --from-file=/mnt/nfs1/prometheus/prometheus.ymlprometheus.yml
global:
scrape_interval: 30s
evaluation_interval: 30s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'lp-kmaster-01'
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.0.183:9100']Grafana-k8.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: grafana-deployment
labels:
app: grafana
env: prod
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: grafana
template:
metadata:
name: grafana-deployment
labels:
app: grafana
env: prod
spec:
containers:
- name: grafana
image: grafana/grafana:7.0.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
ports:
- name: grafana
containerPort: 3000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/grafana
name: grafana-storage
volumes:
- name: grafana-storage
nfs:
server: 192.168.0.184
path: "/opt/nfs1/grafana"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: grafana-service
labels:
app: grafana
env: prod
spec:
selector:
app: grafana
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
nodePort: 30091
HAproxy configuration on docker
1.Install docker
yum install docker
systemctl enable docker
systemctl start docker2. Run haproxy docker images with with persistent volume
mkdir /opt/haproxy
#and move the haproxy.cfg inside /opt/haproxy
docker run -d -p 8888:8888 -p 8404:8404 -v /opt/haproxy:/usr/local/etc/haproxy:Z haproxy3. haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 256
defaults
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 30s
timeout server 30s
log global
mode http
option httplog
maxconn 3000
frontend stats
bind *:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 10s
frontend app1
bind *:80
default_backend app1_backend
backend app1_backend
server server1 192.168.0.151:8080 maxconn 32
server server1 192.168.0.152:8080 maxconn 32
server server1 192.168.0.153:8080 maxconn 32docker-compose file
version: '3'
services:
haproxy:
image: haproxy
ports:
- 80:80
- 8404:8404
volumes:
- /opt/haproxy:/usr/local/etc/haproxySetup elasticsearch cluster with 3 nodes
1. Up the /etc/hosts on all 3 nodes
192.168.0.50 elk1.local
192.168.0.51 elk2.local
192.168.0.52 elk3.localNote : Minimum 2 nodes should be up to make cluster healthy.
2.Install elasticsearch on all 3 nodes
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
echo '[elasticsearch-7.x]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md' > /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo
###install elasticsearch
yum -y install elasticsearch
###Enable elasticsearch
systemctl enable elasticsearch3. Edit /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml as per cluster name (eg. elk-cluster)
cluster.name: elk-cluster
node.name: elk1.local
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
network.host: 192.168.0.50
discovery.seed_hosts: ["elk1.local", "elk2.local", "elk3.local"]
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elk1.local", "elk2.local", "elk3.local"]change the only node.name and network.host for other 2 elasticsearch nodes
4. Restart elasticsearch service on all 3 elasticsearch node
systemctl restart elasticsearchAfter restart 1 master node will be elected.
5. Check master node in elasticsearch cluster
curl -X GET "192.168.0.50:9200/_cat/master?v&pretty"More : https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/cat-master.html
More information about setting up cluster : https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-discovery.html
Pi-hole on kubernetes with NFS persistent volume
1.Create NFS share
2. pi-hole-deployment.yml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pi-hole-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: pi-hole
template:
metadata:
name: pi-hole-deployment
labels:
app: pi-hole
env: prod
spec:
containers:
- name: pi-hole
image: pihole/pihole
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "200m"
volumeMounts:
- name: pihole-nfs
mountPath: /etc/pihole
- name: dnsmasq-nfs
mountPath: /etc/dnsmasq.d
ports:
- name: tcp-port
containerPort: 53
protocol: TCP
- name: udp-port
containerPort: 53
protocol: UDP
- name: http-port
containerPort: 80
- name: https-port
containerPort: 443
volumes:
- name: pihole-nfs
nfs:
server: 192.168.0.184
path: "/opt/nfs1/pihole/pihole"
- name: dnsmasq-nfs
nfs:
server: 192.168.0.184
path: "/opt/nfs1/pihole/dnsmasq.d"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: pi-hole-service
labels:
app: pi-hole
env: prod
spec:
selector:
app: pi-hole
type: NodePort
externalIPs:
- 192.168.0.183
ports:
- name: dns-tcp
port: 53
targetPort: 53
nodePort: 30053
protocol: TCP
- name: dns-udp
port: 53
targetPort: 53
nodePort: 30053
protocol: UDP
- name: http
port: 800
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30054
- name: https
port: 801
targetPort: 443
nodePort: 30055
Note: Use externalIPs in service so that the IP can be put inside wifi DNS.