Error:
Mixed Content: The page at ” was loaded over HTTPS, but requested an insecure stylesheet ”. This request has been blocked; the content must be served over HTTPS.
install nginx with $IP_ADDRESS:8080 version: '3.1'
services:
wordpress:
image: wordpress:6.2.0
restart: always
ports:
- 8080:80
volumes:
- ./wordpress:/var/www/html
db:
image: mysql:5.7.39
restart: always
ports:
- 3310:3306
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
volumes:
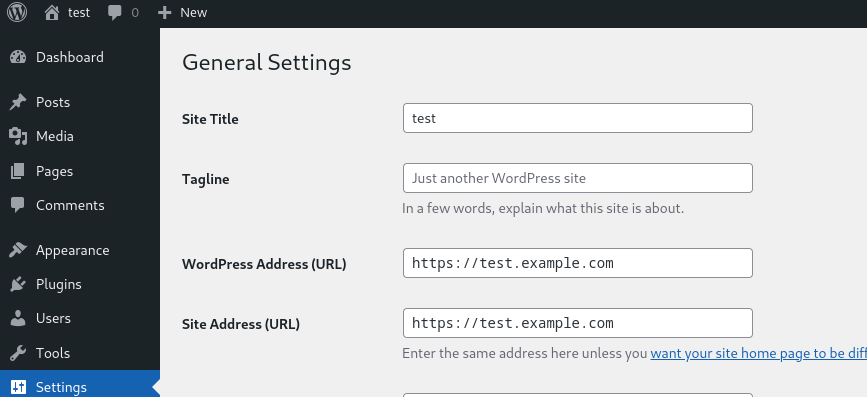
- ./mysql:/var/lib/mysqlUpdate https://test.example.com inside wordpress admin panel define('FORCE_SSL_ADMIN', true);
/etc/nginx/conf.d/test.exmaple.conf nginx config server {
server_name test.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.209.229.54:8080/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 443;
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
}
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/key.pem;
}
server {
if ($host = test.example.com) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server_name test.example.com;
listen 80;
return 404;
}
Reference: