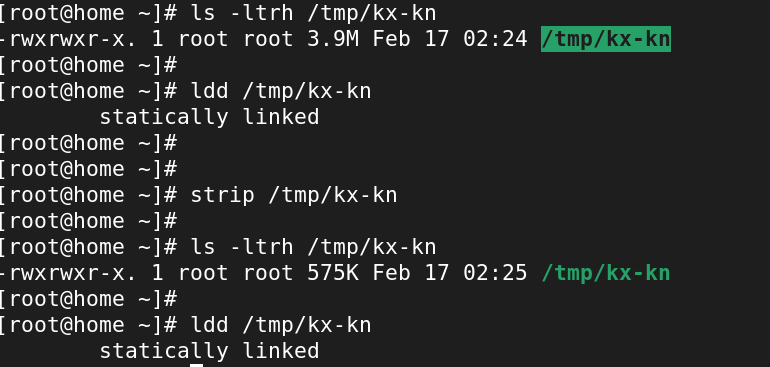
- install openvpn-auth-ldap package
yum install openvpn-auth-ldap- /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
local 192.168.0.183
port 1194
proto udp
dev tun
ca ca.crt
cert server.crt
key server.key
dh dh.pem
auth SHA512
tls-crypt tc.key
topology subnet
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8"
push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.4.4"
keepalive 10 120
cipher AES-256-CBC
user nobody
group nogroup
persist-key
persist-tun
verb 3
crl-verify crl.pem
explicit-exit-notify
plugin /usr/lib/openvpn/openvpn-auth-ldap.so "/etc/openvpn/auth/ldap.conf"
verify-client-cert none
log /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log
log-append /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log- /etc/openvpn/auth/ldap.conf
<LDAP>
URL ldap://ad.example.com:389
BindDN CN=openvpn-svc,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com
Password pass@123
Timeout 15
TLSEnable no
FollowReferrals yes
TLSCACertFile /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
TLSCACertDir /etc/ssl/certs
</LDAP>
<Authorization>
BaseDN "CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com"
SearchFilter "(&(SamAccountName=%u))"
RequireGroup true
<Group>
BaseDN "CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com"
SearchFilter "(cn=openvpn-group)"
MemberAttribute "member"
</Group>
</Authorization>- client-cert.ovpn
client
dev tun
proto udp
remote <publicip> 1194
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
remote-cert-tls server
auth SHA512
cipher AES-256-CBC
ignore-unknown-option block-outside-dns
auth-user-pass
verb 3
<ca>
Masked
</ca>
<cert>
Masked
</cert>
<key>
Masked
</key>
<tls-crypt>
Masked
</tls-crypt>AD powershell command to get user and group details
Get-ADUser -Identity openvpn-svc -Properties *
Get-ADGroup openvpn-group -Properties *
Look at distinguished name and see the correct path